Cultivating plants via a hydroponic system isn’t as challenging as many believe. Notably, basil, a globally renowned herb that features in numerous culinary practices and homes, stands out.
Known for its aromatic allure, basil is one herb that thrives in hydroponic systems.
Let’s learn how to grow your hydroponic basil and explore the tips and techniques that make it possible.
Does Basil Grow Well Hydroponically?
Absolutely! Basil is one herb that adapts splendidly to hydroponics and is easy to grow. When you choose to grow any type of basil hydroponically, you’ll find it grows faster, healthier, and more flavorful than its soil-grown counterpart.
Basil grows well in a controlled environment, making it a favorite among hydroponic growers.
Top Tips for Growing Hydroponic Basil
- Ensure your hydroponic system is clean and free from any pathogens.
- Regularly monitor the pH and nutrient composition of your hydroponic solution.
- Choose the best basil variety for your growing system and conditions.
- Provide basil plants with ample light, preferably from a LED grow light.
- Prune basil leaves periodically to encourage bushier growth.
Benefits of Growing Basil Hydroponically
Choosing to grow basil hydroponically means you’re not only ensuring faster growth but also reaping several benefits. This method, free from soil, reduces the chances of soil-borne diseases.
Growing hydroponic basil is easy at home and guarantees fresh basil leaves at your disposal without the presence of pesticides. Hydroponically grown basil also boasts an enhanced flavor profile, making it a popular choice for many.
Best Hydroponic Systems for Growing Basil
Basil thrives in various hydroponic systems. Choosing the best way to grow often depends on the grower’s resources, space, and experience. Let’s explore the primary types of hydroponic systems and their compatibility with growing basil.
Kratky Method
The Kratky method is a simple form of hydroponics, often dubbed the “set it and forget it” system. It’s passive, meaning it doesn’t require any pumps or electricity.
How it works: Plants are placed in a net pot, which is set into a lid above a reservoir filled with a nutrient solution. The roots dangle into the solution, absorbing the nutrients they need.
As the solution level drops due to uptake and evaporation, the roots grow longer to reach the diminishing water, allowing part of the root system to remain above the water level, accessing atmospheric oxygen.
Why it’s suitable for basil: The Kratky method is beginner friendly and requires minimal equipment. Basil, being a relatively easy-to-grow herb, can thrive in this passive system. However, monitoring the nutrient solution level is vital to prevent the basil from drying out.
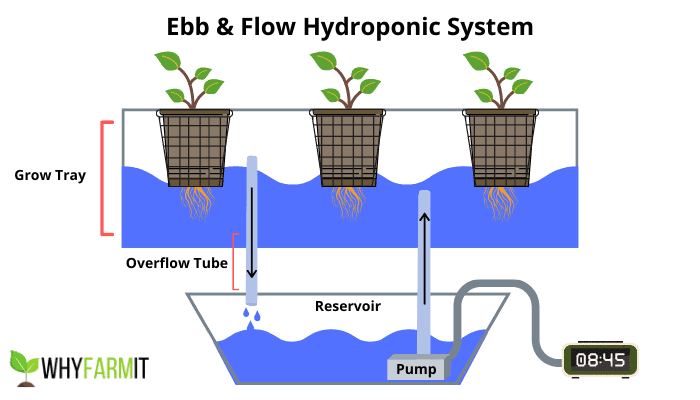
Ebb and Flow Method (Flood and Drain)
The ebb and flow system is a bit more complex than the Kratky method but offers more control over nutrient and oxygen delivery to the plants.
How it works: Plants are situated in a grow bed filled with a growing medium. At scheduled intervals, the grow bed is flooded with a nutrient solution from a reservoir below. After some time, the solution drains back, ensuring the roots don’t remain submerged continuously.
Why it’s suitable for basil: This system ensures that basil roots receive adequate oxygenation, vital for optimal growth. The regular flooding provides consistent moisture, ensuring basil grows well. The periodic draining prevents overwatering and root rot, common issues when growing herbs hydroponically.
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT)
NFT is a popular method for growing smaller, fast-growing plants like basil. It’s efficient and conserves water.
How it works: Plants are placed in net pots in a slightly tilted tray. A thin film of nutrient solution constantly flows over the roots from the higher end of the tray, then drains back into a reservoir to be recirculated.
Why it’s suitable for basil: The constant flow ensures that basil roots receive the nutrients they need without being submerged. It provides a balance of water, nutrients, and oxygen. However, NFT requires consistent monitoring to ensure pumps don’t fail, as roots can dry out quickly without the nutrient flow.
Dutch Buckets
Dutch buckets are versatile and ideal for larger plants but can be used for herbs like basil too.
How it works: Each plant has its bucket filled with a growing medium. A drip system delivers nutrient solution directly to each plant. Excess water drains from each bucket back into the main reservoir.
Why it’s suitable for basil: Dutch buckets allow for ample root space, making them suitable for varieties of basil that grow larger. It offers flexibility in spacing, allowing growers to space basil plants adequately as they mature.
Growing Basil in a Mason Jar
This method combines aesthetics with functionality, making it perfect for home growers who wish to have a decorative touch. Basil will thrive in this simple setup, and it is a very inexpensive option.
How it works: A mason jar or similar glass container is filled with a nutrient solution. Basil seeds or seedlings are placed in a net pot or wool cube that is then placed atop the jar, allowing the roots to access the solution.
Why it’s suitable for basil: Mason jar hydroponics is a minimalist approach, ideal for kitchen countertops or window sills. It allows for a clear view of the root system, which can be both educational and aesthetically pleasing. However, it’s essential to shield the roots from prolonged exposure to light to prevent algae growth.
If you want a done-for-you mason jar herb kit, I’d recommend this one on Amazon.
Best Basil Varieties for Growing Hydroponically
While you can try a variety of basil types in your hydroponic system, some stand out for their growth pattern and flavor.
Genovese Basil

Genovese basil is known for its classic pesto flavor and its cupped, spoon-shaped leaves. It’s the most popular culinary basil variety with dozens of cultivars available.
Some popular choices include ‘Dolly’, ‘Aroma 2’, and ‘Prospera’, all of which are known to be fast-growing and possess benefits like downy mildew resistance.
Italian Large Leaf Basil
Italian Large Leaf is known for being extremely productive. Though it doesn’t tend to grow as tall as Genovese basil, it grows in a bushier fashion.
It has a paler green color and a sweeter flavor profile, so it’s better for dishes that require fresh basil. Its leaves are thicker and more durable than those of Genovese basil.
Popular cultivars of Italian Large Leaf include ‘Nufar,’ ‘Newton,’ and ‘Rutgers Passion DMR.’ ‘Nufar’ in particular is a good choice for hydroponics because it grows quickly and uniformly.
Sweet Basil
Sweet basil is the most popular and widely recognized variety of basil, often associated with Italian cuisine and primarily used for pesto, pasta sauces, and salads.
Sweet basil is characterized by its bright green, oval leaves with a smooth texture. It offers a sweet and slightly peppery taste with hints of clove. When you think of the classic basil taste, sweet basil is likely the variety that comes to mind.
Any Other Basil Variety You Like!
While the varieties listed above tend to be the most popular options for hydroponics, they are certainly not your only options.
Many growers choose specialty varieties like red and purple basil, Spicy Globe basil, Lemon basil, or Sweet Thai basil, but there is no reason your favorite type won’t do well.
Grow what you like! All types of basil will grow hydroponically just as easily as Genovese, Sweet, or Italian Large Leaf basil varieties.
Best Growing Medium for Hydroponic Basil
In hydroponics, the traditional soil is replaced with other mediums that offer better water and air retention, facilitating nutrient uptake.
Selecting the right growing medium ensures that your basil plants have a solid foundation for healthy growth. Here are some popular growing mediums for basil.
- Coconut Coir: Derived from the husk of coconuts, coconut coir offers excellent water retention while providing proper aeration for roots. It’s a sustainable option and has a near-neutral pH. When growing basil hydroponically, coconut coir helps in maintaining consistent moisture, ensuring the roots neither dry out nor remain waterlogged.
- Perlite: This is a volcanic rock that has been super-heated into extremely lightweight, porous granules. Perlite is perfect for hydroponics as it ensures good water drainage and aeration. Often, it’s mixed with other media, like coconut coir or vermiculite, to balance moisture retention and air space.
- Vermiculite: Similar to perlite but with better water retention, vermiculite is a mineral that expands when heated. It can hold a lot of water, making it more suitable for systems where the medium might dry out faster. However, because of its high water retention, it’s usually mixed with perlite to provide better drainage.
- Rockwool: Manufactured from basalt rock and spun into fibrous cubes, rockwool offers excellent air and water retention. Basil seeds can be directly sown into rockwool cubes. However, it’s advisable to wear gloves and a mask as the fibers can be irritative. Also, it’s essential to ensure that rockwool is thoroughly saturated before planting as it can initially repel water.
- Expanded Clay Pellets: These are round, clay pellets that have been heated to form a porous structure. They provide good water and air retention and can be reused after sterilizing. Their heavier weight is beneficial in systems like deep water culture, where they can help plants stay anchored.
Nutrients Needed for Healthy Basil in Hydroponics
To ensure your basil plant grows robustly, the nutrient solution should contain the right balance of primary and secondary macronutrients as well as micronutrients.
- Primary nutrients include nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, all vital for the growth and health of basil.
- Secondary nutrients include calcium, magnesium, and sulfur.
- Essential micronutrients are iron, manganese, boron, molybdenum, copper, zinc, and chlorine.
Investing in a high-quality hydroponic nutrient mix designed for herbs will cater to the basil’s needs.
You can use a foliar-boosting fertilizer like Dyna Gro Foliage Pro to give your basil plants the balanced nutrients they need at the outset, but you should supplement with a Cal Mag supplement as well.
Lighting Requirements for Hydroponic Basil
Basil needs to grow under ample light for robust health and best results. While sunlight is a natural option, many growers opt for LED grow lights as they work well for hydroponic growing, especially when growing indoors.
These lights provide a full spectrum, ensuring the basil leaves develop fully and attain rich flavor. Typically, basil plants need 10-12 hours of light daily for optimal growth.
Best Temperature for Hydroponic Basil
Temperature plays a crucial role in the growth of basil. Basil thrives at temperatures between 70°F and 80°F (21°C – 27°C).
Along with temperature, maintain humidity levels between 40% and 60%. If the environment is too humid, basil is particularly susceptible to fungal infections.
Spacing Requirements for Hydroponic Basil
Spacing your basil plants correctly ensures they get enough airflow, thus reducing the risk of diseases. Ideally, maintain a space of at least 6-8 inches between each basil plant. In systems like NFT, consider the mature size of the plant when spacing seedlings.
Ideal Conditions for Growing Basil in Hydroponics
To grow basil hydroponically with success, consider these ideal conditions:
Starting Basil Seeds for Hydroponic Growing
To grow hydroponic basil, you will need to first start by selecting the best type of hydroponic system for your needs.
Some gardeners choose to clone their basil plants in order to save money on plants, but this can be a time-consuming process.
Another option is to transplant basil plants that were grown in soil into a hydroponic system. However, this can transfer diseases from the soil into your system. Because of this, starting from seed is ideal.
Basil is easy to start from seed and takes just three to 10 days to germinate. While germinating seeds in rapid rooter plugs, keep the temperature around 70-75 degrees Fahrenheit.
You’ll keep them warm like this for the entire time you are growing your plants. I use this germinating system to help maintain consistent temperature and humidity.
Here are the basic steps:
- Soaking: Start by soaking the basil seeds in water for 12-24 hours to expedite germination.
- Planting: Place the soaked seeds onto your chosen growing media. Rockwool cubes are popular and considered the best for basil.
- Environment: Maintain a humidity dome or similar environment to keep humidity levels high.
- Temperature: Keep the growing area at about 70°F (21°C) to support germination.
- Transferring: Once the seedlings develop their second set of leaves, they’re ready to be transferred to your hydroponic system.
How To Grow Hydroponic Basil
Basil is prized for its refreshing taste and versatility in culinary applications, and using a hydroponic system to grow basil at home is an enriching experience. Here’s a guide:
- Select the System: Decide on the type of hydroponic system, such as the Ebb and Flow or NFT.
- Setup: Establish the system according to the manufacturer’s instructions or DIY hydroponic guidelines.
- Nutrient Solution: Prepare a balanced nutrient solution. Regularly monitor and adjust the pH and nutrient composition.
- Planting: Transfer the basil seedlings to the hydroponic garden. Ensure proper spacing.
- Lighting: Use grow lights to provide consistent light if growing indoors.
- Maintenance: Regularly check the basil plants for signs of diseases or pests. Replace the nutrient solution every 1-2 weeks.
Guide To Harvesting Hydroponic Basil
Harvest when the basil plants are dense and produce multiple sets of leaves. Use scissors or shears to cut the basil stems, leaving at least one set of leaves on the plant for regrowth.
Fresh basil leaves can be stored in the refrigerator. Dried basil can be stored for much longer than fresh.
Hydroponic Basil Yield per Plant
A well-maintained hydroponic basil plant can yield between 2 and 4 ounces of fresh basil leaves per plant in a single harvest. With continuous harvesting, this can significantly increase over the life of the plant.
Basil Pests and Diseases
When you grow hydroponic plants, you might think they are entirely safe from pests and diseases since there’s no soil involved, but hydroponic systems aren’t immune.
Unfortunately, basil is popular with several pests and can fall prey to diseases as well. Being proactive can help ensure your basil remains healthy and thriving.
Pests
- Aphids: These tiny green, black, or white pests suck sap from the basil leaves, leading to wilting and a lack of growth. They can be controlled using neem oil or insecticidal soap.
- Spider Mites: These are minuscule arachnids that live on the undersides of leaves. If not addressed, they can cause significant damage. You might notice a fine webbing between leaves. They thrive in hot and dry conditions. Using a neem oil spray can keep them at bay.
- Whiteflies: Whiteflies are small, white-winged pests that sap energy from plants. Their feeding can lead to the yellowing of basil leaves. Sticky traps and natural predators, like ladybugs, can be used to control them.
- Thrips: These are tiny, slender insects that can suck out cell contents, leading to the distortion of leaves and a ruined basil crop. Blue sticky traps can help reduce their numbers.
Diseases
- Fusarium Wilt: This fungal disease affects the basil’s vascular system, leading to wilting and death of the plant. It’s essential to use disease-free seeds and maintain a clean hydroponic system to prevent its spread.
- Downy Mildew: Recognized by the yellow patches on the top of basil leaves and a fuzzy growth underneath, this disease can be combated by maintaining good air circulation and ensuring the leaves remain dry.
- Root Rot: This is a common problem in hydroponics. If basil roots appear dark and mushy instead of white and firm, they might be affected. Regularly checking the nutrient solution’s pH, ensuring proper aeration in the system, and maintaining cleanliness can prevent this.
- Bacterial Leaf Spot: Manifesting as dark, water-soaked spots on the basil leaves, this bacterial issue can spread quickly. Regularly inspecting and removing infected leaves and ensuring proper spacing between plants for adequate air circulation can help manage this problem.
Common Issues and How To Fix Them
Like any plant, basil can face certain challenges in a hydroponic environment. Here are common problems and solutions:
Wilting Basil
Basil wilts because it is dry. It requires frequent watering when grown in the soil. In a hydroponic environment, you may want to increase the frequency at which the solution floods into your system.
You can also upgrade to a larger pot, which will help your basil stop wilting, or mist regularly to increase humidity.
Basil With Yellow Leaves
The most common reason why a basil plant might develop yellow leaves is because of a magnesium deficiency though a nitrogen or zinc deficiency can also be to blame.
Check the nutrient solution you are using, and make sure it is one that meets the specific nutritional needs of basil.
Basil Turning Black
Basil plants turn black when they are suffering from an infestation of bacteria known as Pseudomonas cichorii.
Symptoms include black or brown spots and streaking that eventually encompass the entire plant.
Adding some fans in your grow area can help reduce the spread of this disease as can making sure your plants have proper spacing.
Unfortunately, it’s difficult to get rid of the bacteria once it sets in, so you’ll need to destroy plants that are affected.
Basil Turning Brown
Improper levels of water and a lack of sun can cause a basil plant’s leaves to turn brown and tip downward in a curling fashion. Prune your plant heavily and give your plant more lighting.
Basil Is Flowering
Your basil plant may look beautiful when it flowers, but unfortunately, basil flowers signify that the plant is shutting down vegetative growth and going into reproductive mode.
The leaves will still be edible but the taste will not be as good as if the plant had not yet flowered.
Some growers cut or pinch off flowers to slightly prolong leaf growth (we explain how here), but the end is inevitable. At this point, you can’t do anything besides cut your plant and start again.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Long Does Basil Take To Grow Hydroponically?
From germinating basil seeds to harvest, basil typically takes 4-6 weeks to grow hydroponically, depending on the variety and conditions.
How Long Do Hydroponic Basil Plants Live?
When you grow basil hydroponically, the life span of the plant largely depends on its care and environment. A hydroponic basil plant, under ideal conditions, can continuously produce leaves for 4 to 6 months.
After this period, the plant may become less vigorous and may not yield as many leaves. It’s often due to the natural lifecycle of the basil plant as it reaches maturity and starts focusing on flowering and seeding.
However, with regular harvesting, pinching off the flower buds, and maintaining optimal conditions, you can prolong the productive life of your basil plant.
Can You Regrow Hydroponic Basil?
Yes, you can regrow hydroponic basil from its own cuttings. Here’s a simple guide:
- Select a healthy branch of your existing hydroponic basil plant. Cut a 4-6 inch stem, ensuring it has at least two sets of leaves.
- Remove the lower leaves, leaving only the top set. This ensures that the nutrients and energy go to root development.
- Place the cutting in a container with water. Ensure the cut end is submerged but the remaining leaves are above the water. Within a week or two, you should see roots beginning to form.
- Once the roots are about 2 inches long, the basil cutting is ready to be transferred to your hydroponic system. Treat it as you would a new seedling, ensuring it receives the right nutrient solution and light conditions.
Can You Plant a Hydroponic Basil Plant in Soil?
Yes, a hydroponically grown basil plant can be transferred to soil. Ensure that the roots are gently cleaned and the plant is acclimated gradually to its new environment.
Can You Start Basil From a Cutting?
Absolutely! Take a 4-inch cutting from a healthy basil stem, remove the lower leaves, and place it in water. Once roots appear, transfer to your hydroponic system.
Why Is My Hydroponic Basil Dying?
Several factors can affect your basil’s health, including nutrient imbalances, pests, diseases, and environmental factors. Regularly check the system, pH levels, and nutrient solution for optimal basil production.
Key Takeaways
- Hydroponic basil requires specific light, temperature, and nutrient conditions.
- Proper care and maintenance can prevent most common basil issues.
- Harvesting at the right time ensures flavorful and abundant basil leaves.
- Continuous monitoring and maintenance are the keys to a thriving hydroponic basil garden.


